FAA Lists Airports for 5G Buffer Zones
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has recently unveiled a list of airports that will have buffer zones to mitigate potential interference from 5G wireless signals. This move is part of a broader effort to ensure the safety and reliability of air travel as the deployment of 5G networks continues to expand across the United States. The advent of 5G technology promises faster internet speeds and more reliable connectivity, which are crucial for various sectors, including healthcare, education, and transportation. However, the transition to this advanced technology has not been without its challenges, particularly in the aviation industry.
What Are 5G Buffer Zones?
Buffer zones are designated areas around airports where 5G signals are limited or adjusted to prevent interference with aircraft instruments. These zones are critical because certain frequencies used by 5G networks can potentially disrupt the signals used by aircraft for navigation and communication. The concept of buffer zones is not new; similar measures have been used in other sectors to prevent signal interference. For instance, radio and television broadcast towers often have buffer zones to avoid overlapping frequencies.
The FAA’s decision to implement buffer zones has been met with mixed reactions. On one hand, it addresses concerns about flight safety. On the other, it raises questions about the rollout and effectiveness of 5G technology in these areas. The aviation industry relies heavily on precise and reliable instrumentation, and any potential interference from 5G signals could pose significant risks. Therefore, the FAA’s cautious approach aims to strike a balance between embracing new technology and maintaining the highest standards of safety.
Airports Included in the List
The list of airports that will have 5G buffer zones includes some of the busiest hubs in the country. Here are a few notable ones:
- Los Angeles International Airport (LAX)
- Chicago O’Hare International Airport (ORD)
- Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport (DFW)
- John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK)
- San Francisco International Airport (SFO)
These airports were chosen based on their high traffic volume and the critical nature of their operations. The FAA has been working closely with telecom companies to ensure that these buffer zones are effectively implemented. In addition to these major hubs, several regional airports are also on the list, reflecting the widespread impact of this decision. The inclusion of regional airports underscores the FAA’s commitment to ensuring safety across the entire aviation network, not just in high-traffic areas.
Technical Concerns
The primary concern is the potential for 5G signals to interfere with radar altimeters — crucial instruments that provide data on an aircraft’s altitude. Altimeters operate on frequencies that are close to those used by 5G networks, which could lead to signal overlap and interference. This issue is particularly pressing during critical phases of flight such as takeoff and landing, where precise altitude information is essential. The FAA has conducted extensive testing and research to understand the potential risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
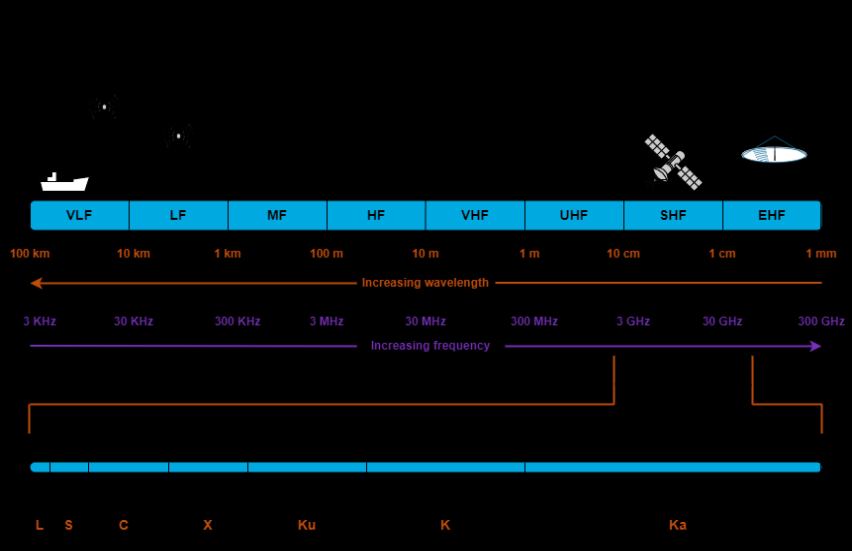
Radar altimeters are especially important during takeoff and landing, when precise altitude information is crucial. Any disruption in these signals could have serious implications for flight safety. Therefore, the FAA’s cautious approach aims to mitigate these risks. The aviation industry has a strong track record of prioritizing safety, and the introduction of 5G technology is no exception. By implementing buffer zones, the FAA is taking a proactive stance to prevent potential issues before they arise.
Impact on 5G Rollout
The implementation of buffer zones around major airports could slow down the deployment of 5G networks in these areas. Telecom companies have invested heavily in 5G technology, and any delays could have financial implications. However, the safety of air travel remains a top priority, and balancing these two interests is crucial. The telecom industry has responded by exploring technical solutions that would allow 5G networks to operate effectively without compromising aviation safety. These efforts include adjusting signal strength, modifying antenna designs, and developing new technologies to minimize interference.
Some industry experts believe that the buffer zones will have a minimal impact on the overall rollout of 5G. They argue that the technology can be adjusted to operate within the constraints set by the FAA without significant degradation in performance. Moreover, the lessons learned from implementing buffer zones around airports could inform best practices for deploying 5G networks in other sensitive areas, such as hospitals and research facilities. This collaborative approach between the FAA and telecom companies highlights the potential for innovation and adaptation in the face of new challenges.
Collaboration Between Industries
The FAA and telecom companies have been working together to address these concerns. This collaboration is essential to ensure that both air travel safety and technological advancement can coexist. Meetings and discussions have been ongoing, with both sides aiming to find a solution that works for everyone. This spirit of cooperation extends beyond technical adjustments; it also involves sharing data, conducting joint research, and fostering open communication between regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders. By working together, the FAA and telecom companies are setting a precedent for how different sectors can collaborate to address complex issues.

One of the proposed solutions is to modify 5G signal strength and direction around airports. This approach would allow 5G networks to function effectively while minimizing the risk of interference with aircraft instruments. Additionally, there are ongoing efforts to develop more robust aircraft instruments that are less susceptible to interference. These advancements could eventually reduce the need for buffer zones, allowing for a more seamless integration of 5G technology in the future.
Public Reaction
The public has had varied reactions to the news of 5G buffer zones. Some people are pleased that the FAA is taking steps to ensure flight safety. Others are concerned about the potential delays in the rollout of 5G technology, which promises faster internet speeds and improved connectivity. The discourse around this issue reflects broader societal debates about the trade-offs between safety, innovation, and convenience. Public opinion is divided, with some arguing that safety should always come first, while others emphasize the economic and social benefits of rapid technological advancement.
Social media platforms have been buzzing with discussions about the FAA’s decision. Many users are sharing their opinions, with some expressing frustration and others showing support. This public discourse highlights the importance of transparent communication between regulatory bodies, industries, and the general public. The FAA and telecom companies have been proactive in addressing public concerns by providing detailed information about the measures being taken and the reasons behind them. This transparency is crucial for building trust and ensuring that the public feels informed and reassured.
Looking Ahead
The FAA’s implementation of 5G buffer zones is a significant step in addressing the potential risks associated with the new technology. As 5G continues to expand, it will be essential to monitor its impact on various sectors, including aviation. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance the compatibility of 5G technology with existing systems, reducing the need for restrictive measures like buffer zones. Innovations in signal processing, frequency management, and aircraft instrumentation are all being explored as potential solutions to the challenges posed by 5G deployment.
Future developments may include advancements in both 5G technology and aircraft instruments to mitigate any potential interference. Research and innovation in these areas will be critical to ensuring that technological progress does not come at the expense of safety. The aviation and telecom industries are already investing in collaborative research initiatives to explore new technologies and develop best practices for the safe and efficient deployment of 5G networks. These efforts are likely to yield valuable insights and solutions that can benefit not only the aviation sector but also other industries that rely on reliable and interference-free communication systems.
Conclusion
The FAA’s decision to create buffer zones around major airports is a precautionary measure aimed at preserving the safety of air travel. While it may pose some challenges for the rollout of 5G networks, the collaboration between the FAA and telecom companies offers hope for a balanced solution. The proactive measures being taken by both industries demonstrate a commitment to finding ways to coexist and thrive in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. As we move forward, it will be essential to continue monitoring the situation and making adjustments as needed. The goal is to achieve a harmonious coexistence between cutting-edge technology and the trusted systems that ensure our safety in the skies.
The ongoing dialogue between the FAA, telecom companies, and the public will play a crucial role in shaping the future of 5G deployment. By fostering open communication and collaboration, we can navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by this new technology. Ultimately, the successful integration of 5G networks will depend on our ability to balance innovation with safety, ensuring that we can enjoy the benefits of faster and more reliable connectivity without compromising the well-being of those who rely on air travel.










